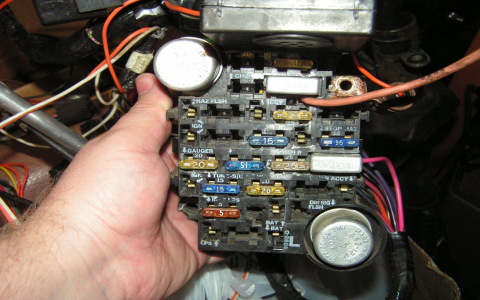
When electrical components fail in your 1999 GMC Sierra, consult the fuse box diagram to identify and troubleshoot issues efficiently. Focus on the primary locations: interior fuse panel (driver's side dashboard) and underhood electrical center (passenger side).
Interior Fuse Panel Diagram Interpretation
Critical fuse identification labels:
- CIGAR (15A): Cigarette lighter/power outlet
- WIPER (25A): Windshield wiper motor and pulse board
- TAIL LP (10A): Taillights, license plate lights
- PWR ACC (30A): Accessory power feed
- CRUISE (10A): Speed control system
Underhood Fuse Center Troubleshooting
High-amperage circuits requiring attention:
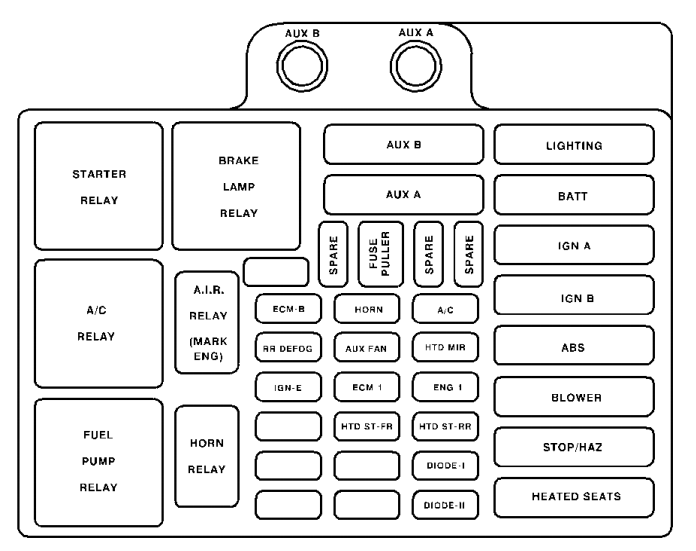
- ABS (60A): Anti-lock brake system (Square Mini Fuse)
- IGN A (40A): Ignition switch feed (Maxi Fuse)
- HEAD LPS (20A each): Left and right headlight circuits
- FAN (40A): Cooling fan relay control
- INJ (20A): Fuel injector power supply
Diagnostic Procedure
Systematic troubleshooting approach:
- Verify component operation with key in both ACC and RUN positions
- Confirm proper fuse box lid diagram correlation to actual fuse slots
- Test suspect fuses with multimeter continuity setting
- Replace blown fuses with identical amperage ratings
- Examine fuse contacts for corrosion requiring electrical cleaner
Common Failure Scenarios
Symptom-based fuse checks:
- No dome light: Check 10A DOME fuse (interior panel)
- Blower motor inoperative: Verify 25A HVAC fuse (underhood)
- Radio memory loss: Test 10A RADIO fuse (interior)
- Non-functional power windows: Inspect 30A PWR WDO fuse (underhood)
- Charge system failure: Examine 15A GEN fuse (interior)
Always disconnect battery ground cable before servicing fuses. Remember that repeated fuse failures indicate underlying circuit problems requiring professional diagnosis.