Access the serpentine belt routing diagram and follow these essential steps for the 2005 Nissan Altima 2.5L (QR25DE engine):
Required Tools
- 15mm wrench or socket with ratchet
- New serpentine belt (e.g., Part Number 6PK2035)
- Mechanic's gloves (recommended)
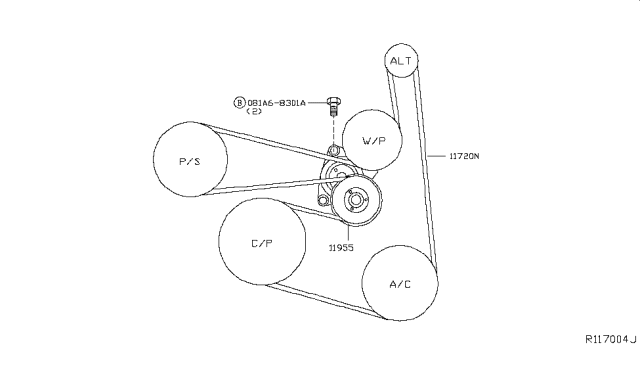
Serpentine Belt Routing Diagram
The belt follows this path around the pulleys:
Crankshaft (Bottom) → A/C Compressor → Idler Pulley → Power Steering Pump → Alternator → Coolant Pump → Tensioner Pulley
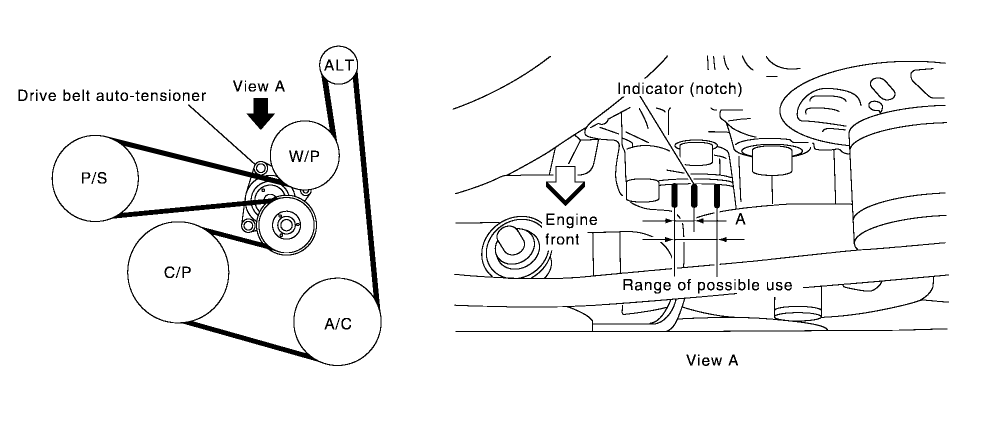
Key: The smooth side of the belt contacts the tensioner and coolant pump pulleys.
Quick Replacement Steps
1. Prepare Vehicle: Park on level ground, engage parking brake, turn engine off, and disconnect the negative battery terminal.
2. Locate Components: Identify all pulleys and the spring-loaded tensioner assembly (typically on driver's side).
3. Release Belt Tension: Insert the 15mm wrench onto the tensioner pulley bolt. Rotate the tensioner clockwise firmly against spring pressure to create slack.
4. Remove Old Belt: Slip the belt off one pulley (usually the alternator) while maintaining tensioner pressure. Carefully guide the entire belt off remaining pulleys.

5. Verify Correct Routing: Double-check the belt diagram above before installing the new belt.
6. Install New Belt: Route the new belt onto all pulleys except the tensioner, ensuring it sits correctly in all grooves. Route it over the tensioner pulley last.
7. Apply Tension: Rotate the tensioner clockwise again to create maximum slack. Slide the belt fully onto the tensioner pulley. Slowly release tensioner pressure.
8. Final Check: Ensure the belt is fully seated in all pulley grooves and properly aligned. Visually confirm routing matches diagram.
9. Reconnect Battery: Reattach the negative battery cable.
10. Test Operation: Start the engine and observe belt operation for 1-2 minutes. Listen for squealing or chirping indicating incorrect tension or routing.
Critical Warnings
Do NOT pry the tensioner body: Apply force only to the central tensioner pulley bolt. Forcing against the tensioner arm can cause failure.
Verify belt seating: Improper routing causes immediate damage. Triple-check the path against the diagram.
Worn tensioners or misaligned pulleys prevent proper tension. Replace faulty components immediately.

