The 5.3 Vortec's plastic intake manifold is prone to specific failure points causing drivability issues. Key diagram areas and associated problems include:
1. Vacuum Leaks (Runner Flange & Port Seals)
Warping and deteriorated gaskets create leaks. Symptoms:
- Rough idle, especially when cold
- Check Engine Light (P0171/P0174 - System Lean)
- High idle or surging
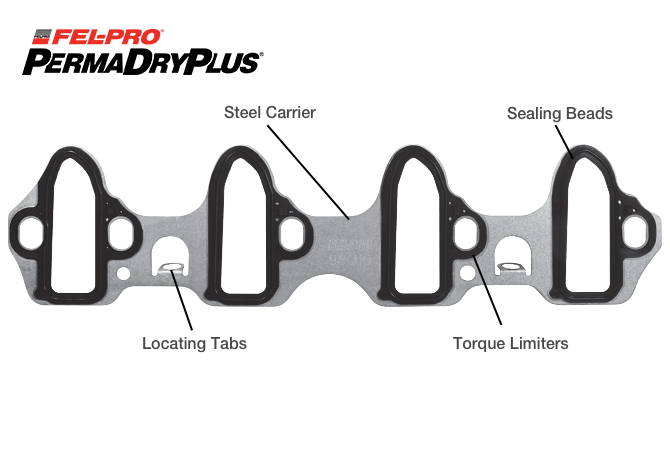
Solution: Inspect manifold flatness. Replace intake manifold gaskets and any cracked hard plastic vacuum lines. Ensure new gaskets are correctly seated.
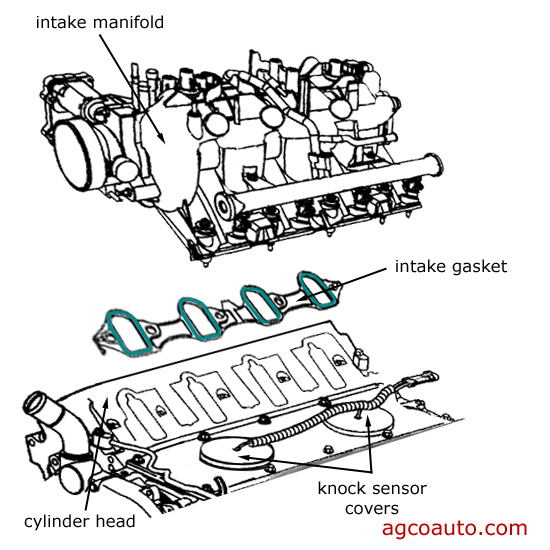
2. Coolant Leaks (Front/Rear Crossover Ports)
Worn or improperly seated gaskets at the manifold-to-head junctions leak coolant into lifter valleys or externally.
- Visible coolant at front/rear of engine
- Low coolant level
- Overheating potential
Solution: Replace manifold gaskets. Clean sealing surfaces meticulously. Use factory-spec torque sequence and values during reinstallation.
3. Cracked Plastic Manifold
Age and heat cycles cause fatigue cracks, often near mounting bosses or coolant ports.
- Vacuum leaks persisting after gasket replacement
- Coolant leaks originating from manifold body
Solution: Carefully inspect manifold, especially near the thermostat housing and heater hose ports. Replace the manifold if cracked.
4. MAP Sensor Port Clogging
The port inside the plenum can accumulate oil/carbon, skewing readings.
- Rough running, hesitation
- Check Engine Light (P0106, P0107, P0108)
Solution: Remove the MAP sensor and inspect/clean the small port in the manifold using appropriate cleaner and soft tools.
5. PCV System (Valley Cover & Breather Ports)
Clogged PCV orifice in the valley cover or manifold baffles causes excessive crankcase pressure and oil consumption.
- Oil consumption
- Oil in intake/throttle body
- May contribute to vacuum leaks
Solution: Clean manifold PCV baffles thoroughly during removal. Ensure updated valley cover with improved PCV orifice.
Troubleshooting Procedure
- Scan for stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Perform a thorough visual inspection for coolant leaks, oil seepage, or obvious cracks.
- Conduct a smoke test to pinpoint vacuum leaks, especially along the manifold sealing surfaces and ports.
- Check manifold surface flatness with a straightedge if leaks are suspected.
- Verify correct PCV system operation and cleanliness.

