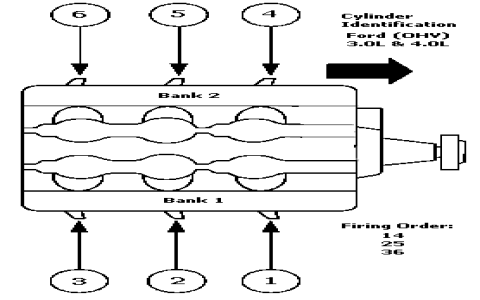
The correct firing order for a 2000 Ford Ranger's 4.0L V6 engine is crucial for smooth, efficient, and reliable operation. Deviating from this sequence directly leads to misfires and associated problems.
Function of Firing Order
Firing order dictates the sequence in which spark plugs ignite the air-fuel mixture in each cylinder. The 4.0L V6's specific order (1-4-2-5-3-6) is engineered to:
- Ensure optimal crankshaft rotation balance, minimizing torsional vibration.
- Distribute engine loads evenly across the crankshaft bearings.
- Maintain proper exhaust pulse scavenging.
- Ensure the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) receives predictable signals from the crankshaft position sensor (CKP) and camshaft position sensor (CMP) for precise ignition timing and fuel injection control.
Consequences of Incorrect Firing Order
Installing spark plug wires in the wrong sequence disrupts engine function, primarily causing:

- Severe Engine Misfires: Spark occurs at the wrong time, preventing combustion in some cylinders or causing partial/failed burns in others.
- Rough Idle & Hesitation: Unbalanced power delivery creates significant vibration.
- Loss of Power & Performance: Multiple cylinders not firing correctly drastically reduces engine output.
- Increased Emissions & Fuel Consumption: Unburned fuel enters the exhaust system.
- Illuminated Check Engine Light (CEL): Misfire detection triggers Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) like P0300 (random misfire) and specific cylinder codes (P0301-P0306).
- Potential Catalytic Converter Damage: Prolonged misfires allow raw fuel into the hot catalytic converter, causing overheating and premature failure.
- Risk of PCM/Sensor Confusion: Erratic signals can confuse the PCM, potentially leading to broader drivability issues.
Why Specifically Important for the 4.0L Ranger
Knowing the precise order (1-4-2-5-3-6) matters because:
- V6 Configuration: The arrangement of cylinders (front: Passenger 1-2-3, Driver 4-5-6) demands this specific sequence for balance.
- Distributorless Ignition System (DIS): While lacking a central distributor, the coil pack output terminals MUST connect to the correct spark plugs via wires following this sequence. Misrouting wires is a common mistake.
- Precise Sensor Synchronization: The CKP and CMP signals correlate to the expected firing order. Incorrect firing disrupts the PCM's calculated timing.
Avoiding Misfires: Key Practices
- Verify Cylinder #1 Position: Always confirm cylinder #1 location (frontmost passenger side) before connecting wires.
- Follow Manufacturer Specifications: Consult repair manuals or underhood diagrams explicitly for the 2000 Ranger 4.0L, as firing orders differ between engines. Use the sequence: 1-4-2-5-3-6.
- Replace Wires Methodically: Change spark plug wires one at a time to preserve the correct routing order.
- Inspect Components: Ensure wires are undamaged, properly seated on plugs and coil terminals to prevent arcing or poor connection.
- Scan for Codes: If misfires occur after service, scan for DTCs to pinpoint affected cylinders and verify wire routing.
Adhering strictly to the designated 1-4-2-5-3-6 firing order is paramount to preventing misfires and ensuring the engine operates as designed, delivering performance, efficiency, and longevity.