Understanding Chevy Transfer Case Issues
Chevrolet transfer cases facilitate power distribution in 4WD or AWD systems. Problems often stem from component wear or fluid issues, leading to drivability concerns. Early diagnosis with a transfer case diagram prevents costly repairs.
Common Problems and Symptoms
- Fluid leaks: Resulting from damaged seals or gaskets, causing unusual noises or shifting difficulties.
- Shifting failures: Due to electronic malfunctions or mechanical binds, limiting mode changes.
- Noises like grinding or whining: Indicating bearing wear, chain slippage, or internal gear damage.
Diagnostic Steps Using Diagrams
Access your Chevy's transfer case diagram to pinpoint parts. Perform visual and physical checks: measure fluid levels for contamination, listen for unusual sounds during operation, and test shift linkages or electronic controls for resistance. This guides targeted interventions.
Fixing Common Issues
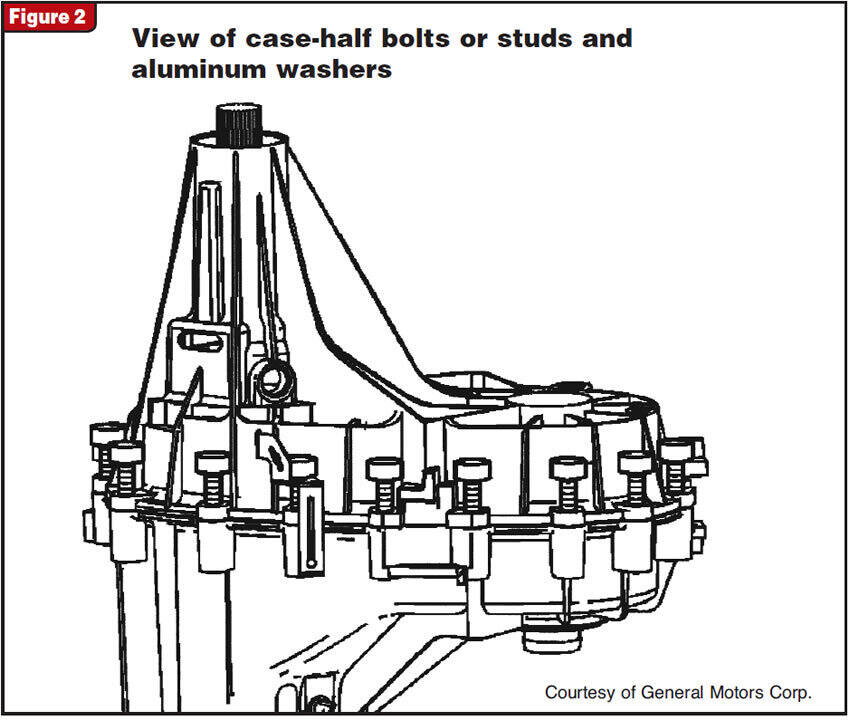
Address leaks by replacing seals or gaskets after referencing the diagram for alignment. For shifting problems, inspect and repair wiring harnesses or actuators. Persistent noise may require bearing or chain replacement; follow torque specs in diagrams to prevent assembly errors.
Preventive Maintenance
Routinely change fluid and inspect seals per your model's transfer case diagram. Schedule electronic system diagnostics to avoid recurrence.