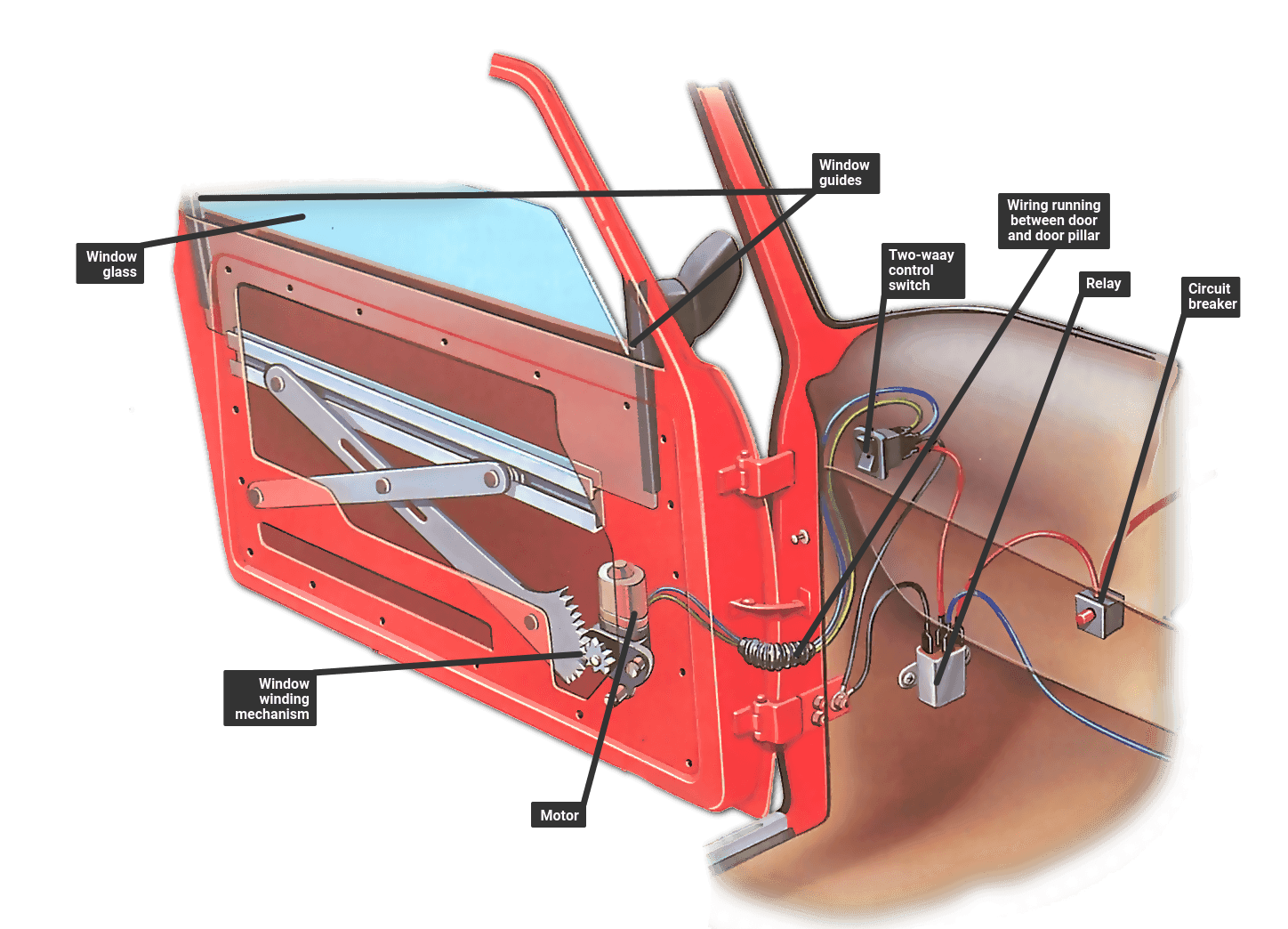
Understanding the power window motor and its associated components is crucial for diagnosing and repairing window failures. Below is a guide to the essential parts you'll encounter.
Core Power Window System Components
An electric car window system primarily consists of:
- Window Motor: The electric DC motor providing rotational force. Located inside the door panel.
- Regulator Assembly: Translates the motor's rotation into vertical window glass movement.
- Master Control Switch: Panel on the driver's door controlling all windows.
- Individual Window Switches: Located on respective doors for passenger control.
- Wiring Harness: Network of wires delivering power and control signals throughout the system.
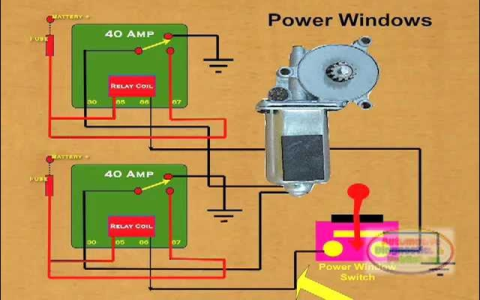
- Fuse/Relay: Protects the circuit from overloads.
Window Motor & Regulator Function
The motor has an output shaft connected to the regulator. Inside the motor housing, brushes conduct electricity to the armature, creating the magnetic field that spins it. This rotation engages with the regulator mechanism. Common regulator types include:
- Cable Regulator: Uses a motor-driven drum winding/unwinding a steel cable attached to the window bracket.
- Scissor Regulator: Features linked metal arms that extend/retract to raise/lower the glass.
- Rail Regulator: Employs a plastic carrier sliding along a metal track, driven by a cable or gear.
Switch & Control System Operation
When you press a window switch:
- It sends a signal (often via the master control module for driver commands).
- The control circuit activates the relevant relay.
- Power flows through the harness to the specific window motor.
- The motor reverses polarity depending on the "Up" or "Down" command, changing its rotation direction.
- The regulator converts this rotation into linear motion for the window glass.
Common Failure Points
Use this diagram knowledge to troubleshoot:
- Window Won't Move (No Sound): Likely no power. Check fuse first. Test for power at the motor plug with a multimeter when the switch is pressed.
- Window Won't Move (Motor Hums): Motor gets power but can't move. Suspect a jammed regulator, broken cable, detached plastic carrier, or seized scissor arms. Requires door panel removal.
- Slow/Intermittent Movement: Often worn motor brushes, internal motor fault, deteriorating wiring, poor switch contacts, or binding in the regulator track/glass run channel.
- One Switch Doesn't Work: Problem likely isolated to that specific switch or its wiring.
- Motor Works One Way Only: Faulty switch contacts, wiring break in one direction's circuit, or potentially a motor issue.
Safety & Repair Tips
- Disconnect the vehicle battery before working near wiring or removing the motor.
- Access requires careful removal of the interior door panel.
- Support the window glass securely with tape across the top of the door frame before disconnecting the regulator to prevent shattering.
- The motor and regulator are often serviced as a single, pre-assembled unit for reliability.
- Diagnostics require a multimeter and potentially access to wiring diagrams specific to the vehicle make/model/year.