Locating the precise serpentine belt diagram for your Subaru requires matching exact model year and engine specifications due to routing variations across generations. Avoid reliance on generic guides, as incorrect tensioner positioning or accessory placement risks premature belt failure.
Verifying Vehicle Specifications
Confirm these details before searching:
- Model & Trim (e.g., 2018 Outback 3.6R Limited)
- Engine Displacement (2.0L, 2.5L, 3.6L, etc.)
- Accessory Package (presence of secondary air pump or heavy-duty alternator alters routing)
Manufacturer service manuals or dealership VIN decoders provide definitive configuration data.
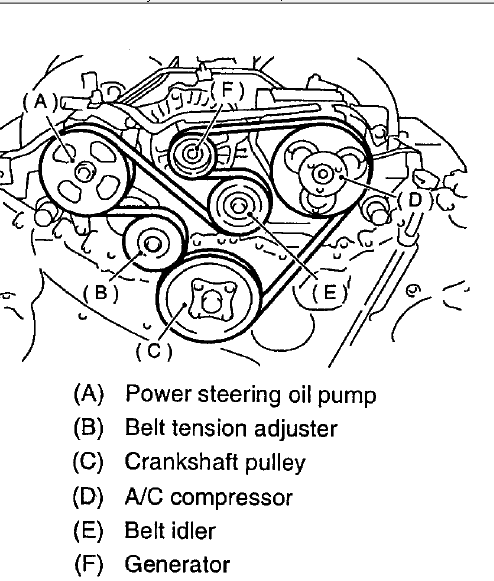
Standard Routing Configurations
Common patterns for popular platforms:
- FB/FA Engines (2012+ Impreza/Crosstrek): Water pump-driven tensioner with idler pulley near A/C compressor.
- EJ25 Turbo (WRX/STI): Spring-loaded automatic tensioner above alternator, auxiliary idler below power steering pump.
- EZ36 (Ascent/Tribeca) Dual-path routing with crankshaft harmonic balancer separation.
Component positions vary between naturally aspirated and turbocharged variants.
Installation Verification Protocol
After belt replacement:
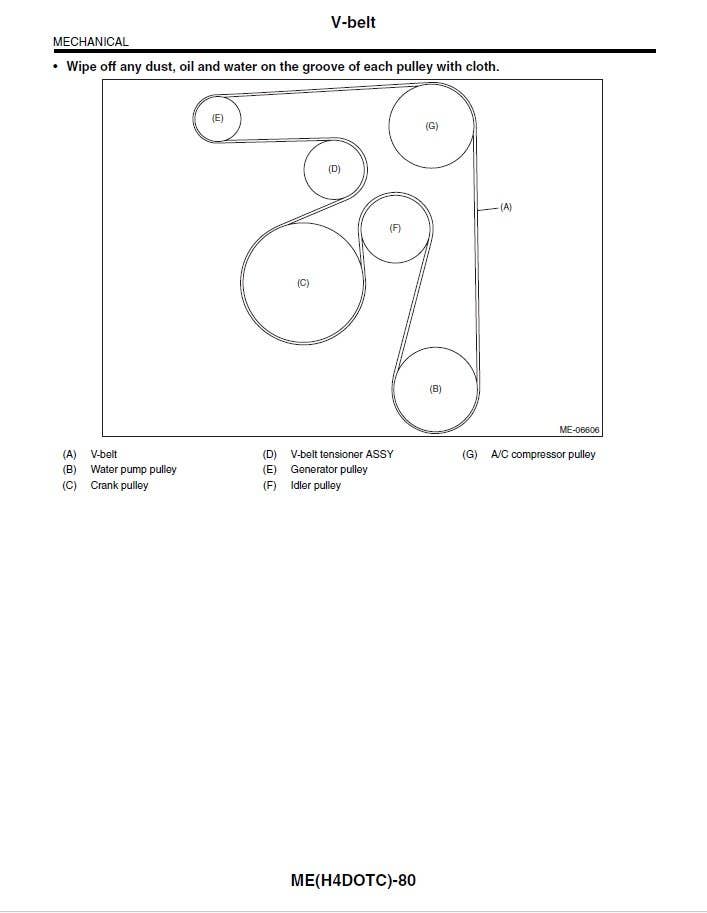
- Rotate crankshaft pulley clockwise 2 full revolutions by hand
- Inspect rib alignment on all pulleys under tension
- Verify automatic tensioner indicator mark remains within operational range
- Check for high-frequency vibration at 2000-3000 RPM indicating misrouting
Cross-referencing against OEM technical service bulletins prevents known configuration errors.
Service documentation from Subaru TIS or factory-authorized repair databases supersedes aftermarket references. Always match diagram production dates to your vehicle's build month/year for accessory revisions.

