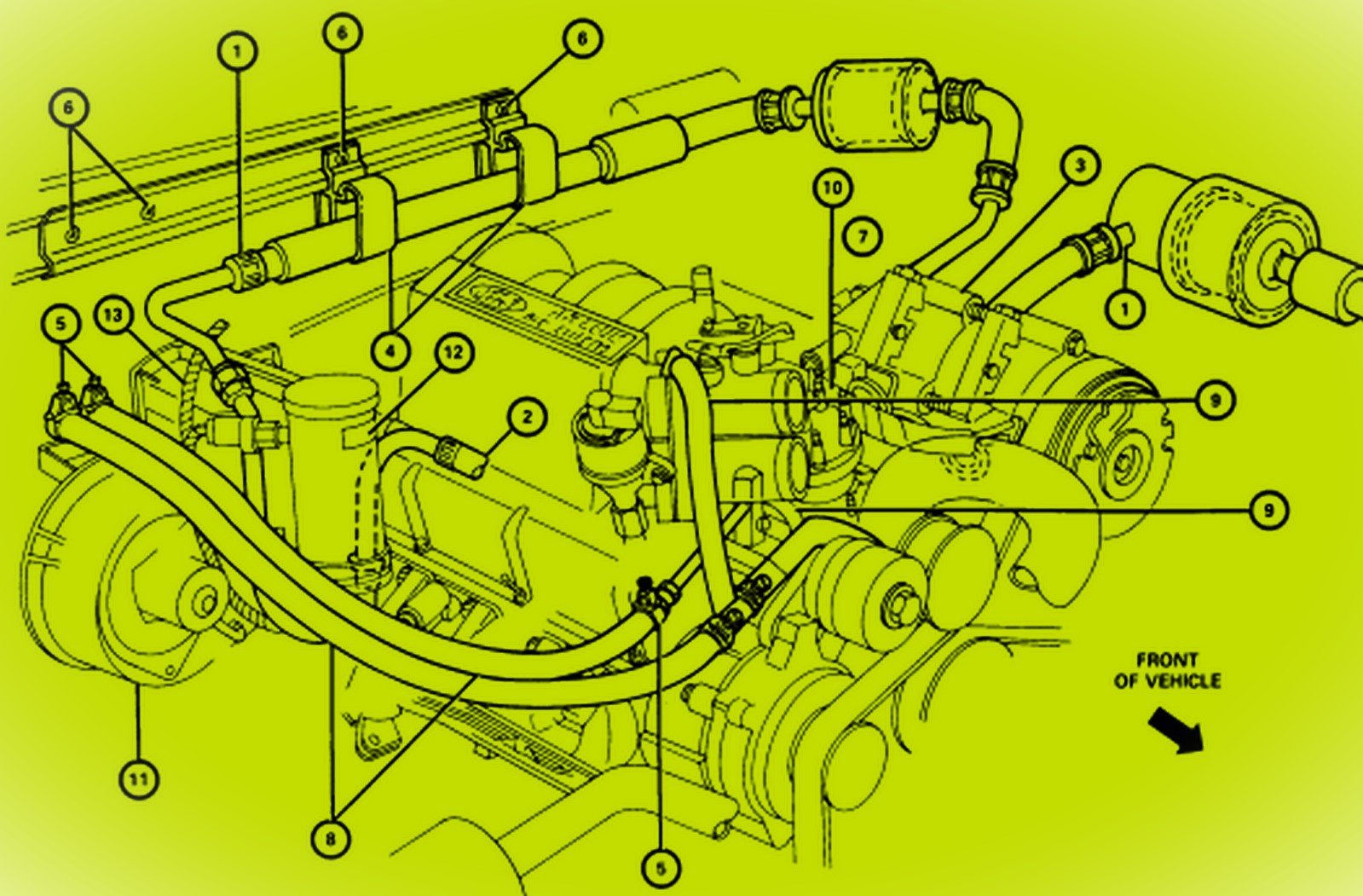
Interpreting a 5.4L Triton engine heater hose diagram requires understanding coolant flow paths and component identification. Follow these steps:
Identify Critical Components
- Heater Core Tubes: Two metal tubes protruding through the firewall (passenger side).
- Heater Control Valve (HCV): Vacuum-operated valve near the brake booster controlling flow.
- Bypass Hose: Short hose connecting intake manifold to water pump when HCV is closed.
- Thermostat Housing: Central connection point near the engine's front.
- Quick Connect Fittings: Common at core tubes and HCV.
Trace Hose Routing & Flow
Supply Hose:
- Originates at the thermostat housing (upper driver side port common).
- Connects to the INLET of the Heater Control Valve (HCV).
- Transports hot coolant from the engine toward the heater core.
Outlet Hose:
- Connects from the OUTLET of the heater core tubes.
- Returns cooled coolant to the water pump (usually via a lower intake manifold port or pump nipple).
Bypass Hose:
- Runs directly from the HCV outlet (or a dedicated port near the thermostat housing) to the water pump or intake manifold inlet port.
- Activates when the HVAC is set to cold, bypassing the heater core.
Diagram Interpretation Tips
- Arrows: Indicate coolant flow direction.
- Labels: Look for "IN" and "OUT" markings on the HCV and heater core connections.
- Vacuum Line: The HCV vacuum line solenoid is shown - connects HVAC control vacuum.
- Hose Identification: Diagrams often use specific colors or dashed patterns for clarity.
- Physical Features: Hoses may have stripes indicating direction.
Key Considerations
- Correct Routing: Improper hose connection prevents defrost/heat operation and can cause overheating.
- Quick Connects: Use proper tools to avoid damaging fittings.
- Heater Control Valve Function: If blocked, heater core doesn't receive flow. If stuck open, heat may always be present.
- Model Year: Routing may vary slightly between generations (e.g., early vs late 5.4L). Compare diagram to your engine.
- Vacuum Supply: Loss of vacuum disables the HCV.
Match hoses based on destination ports and flow direction. Diagrams are vehicle-specific – ensure yours matches your model year.

