Maintaining precise torque specifications is critical for the longevity and performance of your Master Dodge 2.4L engine. Here are the essential specs and professional tips:
Cylinder Head Bolts
Tightening Sequence & Torque: Follow the manufacturer's specific multi-step angular torque sequence precisely.
- Initial: 30 ft-lbs (40 Nm)
- Final: Apply additional 90 degrees turn + another 90 degrees turn (Total 180 degrees).
Critical Tip: Clean bolt threads and holes meticulously. Apply engine oil to bolt threads and under bolt heads only if specified in your service manual. Use a calibrated torque wrench with angle gauge.
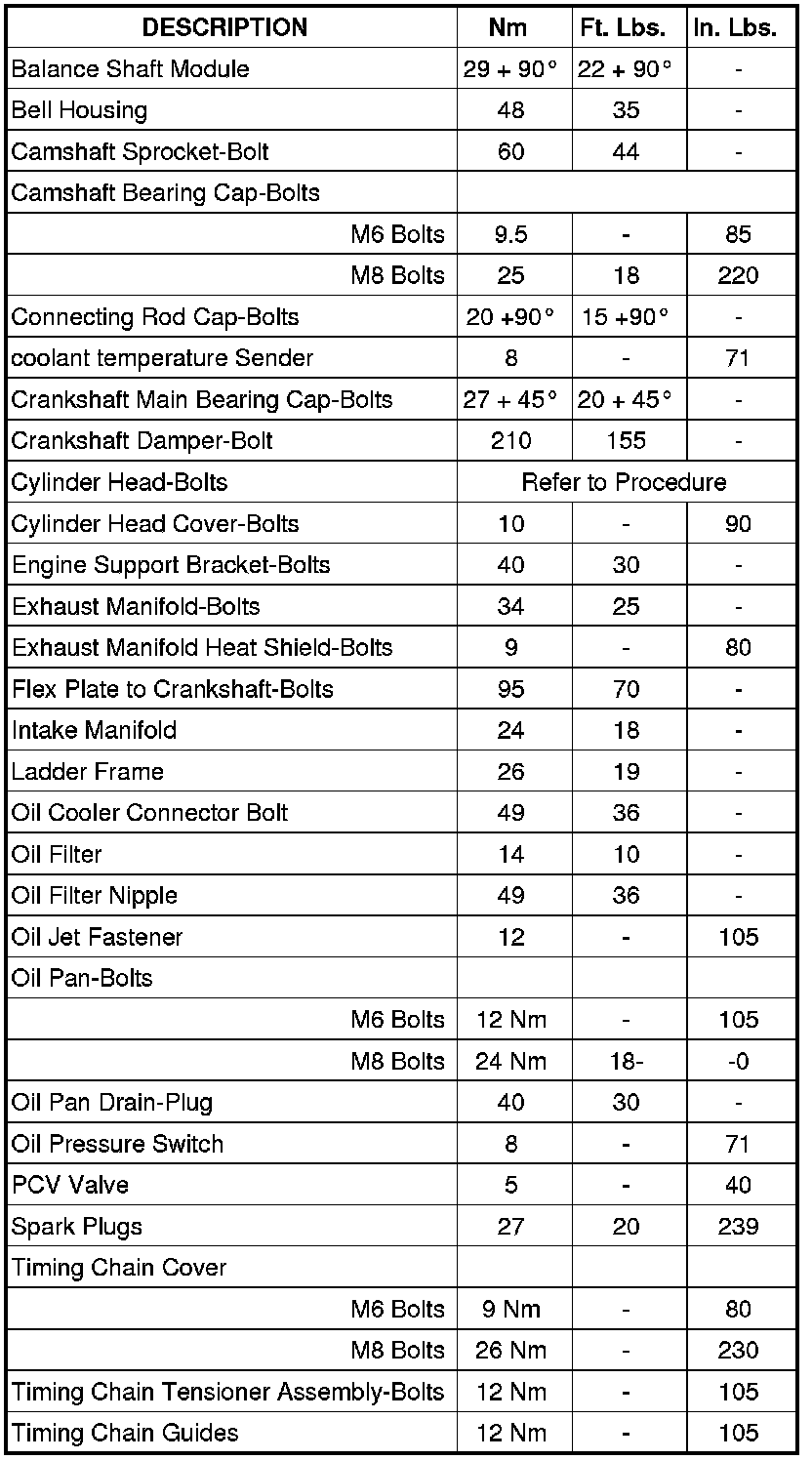
Main Bearing Cap Bolts
- Torque: 50 ft-lbs (68 Nm)
Critical Tip: Ensure bearing caps and block surfaces are spotless and lubricated with clean engine oil before assembly. Torque evenly and progressively in the specified sequence.
Connecting Rod Cap Bolts/Nuts
- Torque: Oil threads and nut seats: 25 ft-lbs (34 Nm) + Additional 75 degrees turn.
Critical Tip: Use only new stretch bolts. Torque-to-angle specifications are non-negotiable for correct bearing crush.
Camshaft Sprocket Bolt
- Torque: Clean & dry: 50 ft-lbs (68 Nm) + Additional 60 degrees turn. (Verify specific year/model variant)
Critical Tip: Lock the camshaft using the proper tool, never via the cam itself. Dry threads are typically required for accurate clamping force.
Oil Pump Mounting Bolts
- Torque: M8 Bolts: 22 ft-lbs (30 Nm)
Critical Tip: Apply thread locker as specified. Ensure the pump pickup tube is correctly seated to prevent oil starvation.
Oil Pan Bolts
- Torque: 106 in-lbs (12 Nm)
Critical Tip: Use a new gasket or approved RTV sealant. Follow the recommended tightening pattern starting from the center, working outwards in stages. Overtightening distorts the pan flange.
Intake Manifold
- Torque: 106 in-lbs (12 Nm) in specified sequence.
Critical Tip: Clean mating surfaces thoroughly. Ensure old gasket material is completely removed without scoring the surfaces.
Exhaust Manifold Bolts/Nuts
- Torque: 19 ft-lbs (26 Nm)
Critical Tip: Inspect for warpage. Apply anti-seize compound sparingly to the bolt threads (avoid contact with nut threads/faces). Tighten in sequence from the center outwards to prevent cracking.
Spark Plugs
- Torque: Clean threads: 156 in-lbs (17.6 Nm)
Critical Tip: Always use a thread chaser to clean the cylinder head threads before installation. Hand-thread the plugs carefully to avoid cross-threading.
Oil Filter
- Torque: Hand-tighten + 3/4 turn after gasket contacts the block. Plastic housing: Follow manufacturer's specific low torque requirement carefully.
Critical Professional Reminders
- Reference First: Always consult the latest service manual for your specific model year and variant; specifications and procedures can change.
- Fastener Integrity: Inspect all bolts, especially torque-to-yield (TTY) bolts like head and rod bolts. Reuse TTY bolts is generally not recommended. Replace with factory-approved new bolts.
- Cleanliness: Debris in threads causes false torque readings and improper clamping force.
- Proper Lubrication: Apply lubricant (oil, specific lube) to bolt threads only when explicitly instructed. Dry and lubricated specs differ significantly.
- Calibrated Tools: Use a well-maintained, calibrated torque wrench. For angle torquing, a reliable angle gauge is mandatory.
- Sequence & Stages: Follow bolt-tightening sequences meticulously and torque in multiple stages.
Warning: Tapered Bolts (e.g., certain manifold bolts): These often have unique torques. Misinterpretation leads to broken bolts.