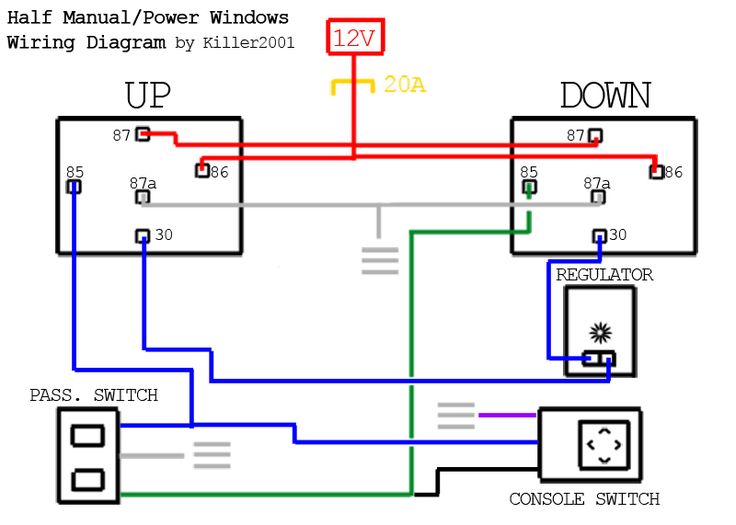
Power window systems are essential in modern vehicles, relying on a straightforward wiring schematic that allows for easy DIY diagnostics and repairs. This guide breaks down the key components and provides simple interpretations to empower your fix-it efforts.
Basic Wiring Components Explained
- Motor: Operates the window mechanism with two terminals for directional control (e.g., A for up, B for down).
- Switch: Features multiple terminals (input power, outputs to motor, and ground) to toggle window movement.
- Relay: Optional in some designs for handling higher current loads; acts as an electrical switch.
- Fuse: Located near the power source to prevent circuit damage from overloads.
- Power Source: Typically the vehicle battery (12V DC), with positive and negative connections.
Simple Wiring Schematic Breakdown
A standard schematic includes the battery positive terminal connected through a fuse to the switch input. From here, the switch has two output paths: one set for raising the window (e.g., connecting motor terminal A to power and motor terminal B to ground) and another for lowering (reversing the connection). The motor is wired so that each terminal completes the circuit through ground when activated, enabling bidirectional motion.
Interpreting the Diagram for DIY
Read the schematic as a visual flow: battery symbol, fuse symbol, switch with labeled terminals (e.g., B+ for power input), motor symbol with A and B points, and ground connection. When a switch direction is engaged, current flows from power through the fuse to the motor, returning via ground. Test for continuity or voltage drops to diagnose issues.
Common DIY Fixes and Troubleshooting
- Motor Fails to Operate: Check fuse continuity with a multimeter; replace if blown. Test switch terminals for proper output when pressed.
- Window Stuck in One Direction: Inspect wiring between switch and motor for breaks or shorts; repair or replace damaged sections.
- Intermittent Operation: Clean switch contacts or test relay functionality; weak connections often cause this fault.
Critical Safety Precautions
- Disconnect Battery Immediately: Always before touching wiring to avoid shocks or shorts.
- Use Insulated Tools: Prevent accidental grounding or circuit damage during testing.
- Refer to Vehicle Manual: Schematics vary by model; ensure compatibility.
